
Bees and wasps are both vital to the ecosystem, especially as pollinators. However, they can become problematic when their nests are built near homes or businesses. While these insects share similarities, understanding their differences is crucial for managing them safely and effectively. This guide explores the difference between wasps and bees, their appearance, diet, nesting habits, and stings, while also highlighting the most common species you might encounter and how to deal with infestations.
Difference Between Wasps and Bees
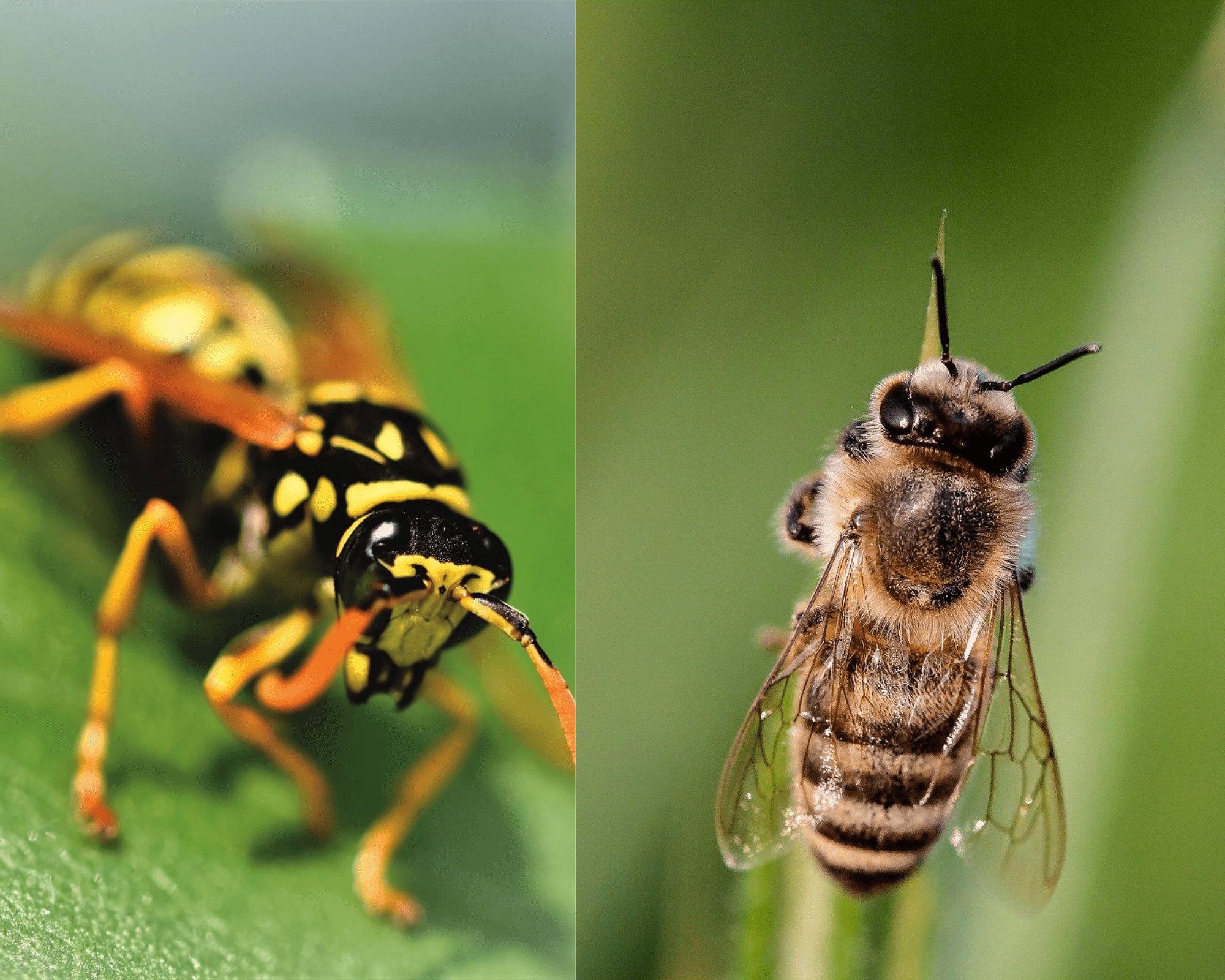
Although both bees and wasps are stinging insects and play critical roles in pollination, they differ significantly in several ways. Below, we break down the differences between wasps and bees into specific categories.
Appearance
The most noticeable difference between wasps and bees is their appearance:
- Bees: Bees are round-bodied with soft, fuzzy hair that helps them collect pollen. Their head, thorax, and abdomen appear to blend together smoothly. Bees have flat, hairy legs designed to carry pollen. When in flight, they tuck their legs close to their bodies.
- Wasps: Wasps have slender, segmented bodies with a distinct, narrow waist. Their smooth, shiny bodies lack visible hair. Unlike bees, wasps let their cylindrical, hairless legs hang down while flying.
These physical traits make it easy to identify wasps vs bees at a glance.
Diet
Bees and wasps differ significantly in their dietary habits, reflecting their ecological roles:
- Bees: Bees are herbivores that feed on nectar and pollen. Their hairy bodies allow them to collect and transfer pollen between flowers, making them essential for pollination.
- Wasps: Wasps are both pollinators and predators. While they feed on nectar, they also hunt other insects, spiders, and larvae to feed their young. This carnivorous behavior makes wasps beneficial for pest control but contributes to their aggressive tendencies.
Nests
The difference between wasp and bee nests lies in their construction and location:
- Bees: Honey bees construct wax hives with honeycomb structures, often in tree cavities, eaves, or sheltered spaces. Bumblebees build nests near the ground in woodpiles or abandoned rodent burrows.
- Wasps: Wasps, including hornets and yellow jackets, build nests from a paper-like material made from chewed wood fibers. Hornet nests vs wasp nests vary in size and location, with hornets building large, enclosed nests in high places and yellow jackets often nesting near the ground. Paper wasps create smaller, umbrella-shaped nests in trees or eaves.
Bee and Wasp Stings
The anatomy of stingers and their behavior are key differences:
- Bees: Bees have barbed stingers that remain embedded in their target, leading to the bee's death after stinging. Bee stings are less likely unless the bee feels threatened.
- Wasps: Wasps, including hornets and yellow jackets, have smooth stingers that allow them to sting multiple times. Wasps are more aggressive and likely to sting without provocation, particularly when their nests are disturbed.
If you find a stinger in a sting site, it likely came from a bee. If no stinger remains, the culprit was probably a wasp.
Commonly Seen Bees and Wasps
Bees
- Bumblebees: Bumblebees are black and yellow with a hairy appearance. They range from ¼ to 1 inch in size and typically nest near the ground, often in woodpiles or compost heaps.
- Carpenter Bees: Carpenter bees resemble bumblebees but have shiny, hairless black abdomens. They drill into softwood to create segmented tunnels for their nests and are most active in warm months.
- Honey Bees: Honey bees are smaller, about 15 mm long, with mustard-yellow and brown coloring. They build waxy, honeycomb hives and are critical for pollinating gardens, orchards, and crops.
- Sweat Bees: Sweat bees are small, slender, and metallic green or brown. They nest underground and are attracted to human sweat but rarely sting unless provoked.
Wasps
- Hornets: Hornets are large wasps with enclosed nests found in high locations like treetops or roofs. Bald-faced hornets are black and white, while European hornets are reddish-brown and yellow.
- Yellow Jackets: Yellow jackets are aggressive wasps with yellow and black banding. They build nests near the ground and are known for scavenging human food.
- Mud Daubers: Mud daubers are solitary wasps that build nests of mud tubes, often in attics or ceilings. They are less aggressive than social wasps.
- Paper Wasps: Paper wasps construct umbrella-shaped nests and are often found in trees or eaves. They are social insects with reddish-brown or yellow coloring.
Wasp and Bee Control
While bees and wasps play essential roles in ecosystems, their nests near homes or businesses can pose safety risks. Attempting to remove nests yourself is dangerous, as these insects can become aggressive when threatened.
Why Choose Excel Pest Services?
At Excel Pest Services, we specialize in the safe and effective removal of wasp and bee nests. Whether you’re dealing with a hornet nest vs wasp nest, yellow jacket infestation, or need help identifying the issue, our experienced team is here to help.
- Environmentally Friendly Methods: We prioritize solutions that protect both your property and the environment.
- Experienced Professionals: With years of expertise, we ensure safe removal and prevention of future infestations.
- Tailored Solutions: Every situation is unique, and we customize our services to meet your specific needs.
Don’t let a bee or wasp problem disrupt your peace of mind. Contact Excel Pest Services today to schedule an inspection and reclaim your space!
Understanding the difference between wasps and bees is crucial for managing their presence safely and effectively. Bees are vital pollinators that should be preserved whenever possible, while wasps contribute to pest control but can become aggressive. Identifying their unique traits helps you respond appropriately to any situation.
When nests pose risks to your home or business, trust Excel Pest Services for safe and efficient removal. With professional expertise and environmentally friendly practices, we ensure your property remains safe and pest-free. Call us today to learn more about our services and protect your space from unwanted pests!
Frequently Asked Question:
What are the Key Differences Between Wasps, Bees, and Hornets
- Hornet vs Wasp: Hornets are a type of wasp but are generally larger and build larger, enclosed nests. Wasps are more common and include species like yellow jackets and paper wasps.
- Yellow Jacket vs Wasp: Yellow jackets are a type of wasp known for their aggression and preference for scavenging human food. They build nests near the ground, unlike other wasps.
- Bee vs Wasp vs Hornet: Bees are pollinators with hairy, round bodies, while wasps and hornets are predators with smooth, slender bodies. Hornets are larger than most wasps.
- Hornet vs Wasp vs Yellow Jacket: Hornets are larger than yellow jackets and wasps. Yellow jackets are more aggressive and nest closer to the ground, while hornets prefer elevated locations.
- Bee Sting vs Wasp Sting vs Hornet Sting: Bee stings involve barbed stingers that stay in the skin, while wasps and hornets have smooth stingers that allow multiple stings. Hornet stings are the most painful due to their size and venom potency.
By understanding these differences, you can identify and manage these insects more effectively, ensuring safety for you and your loved ones.






